




 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|---|---|
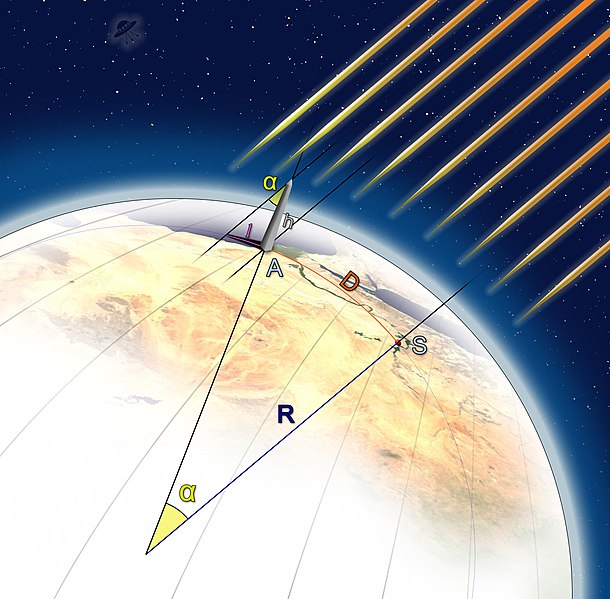
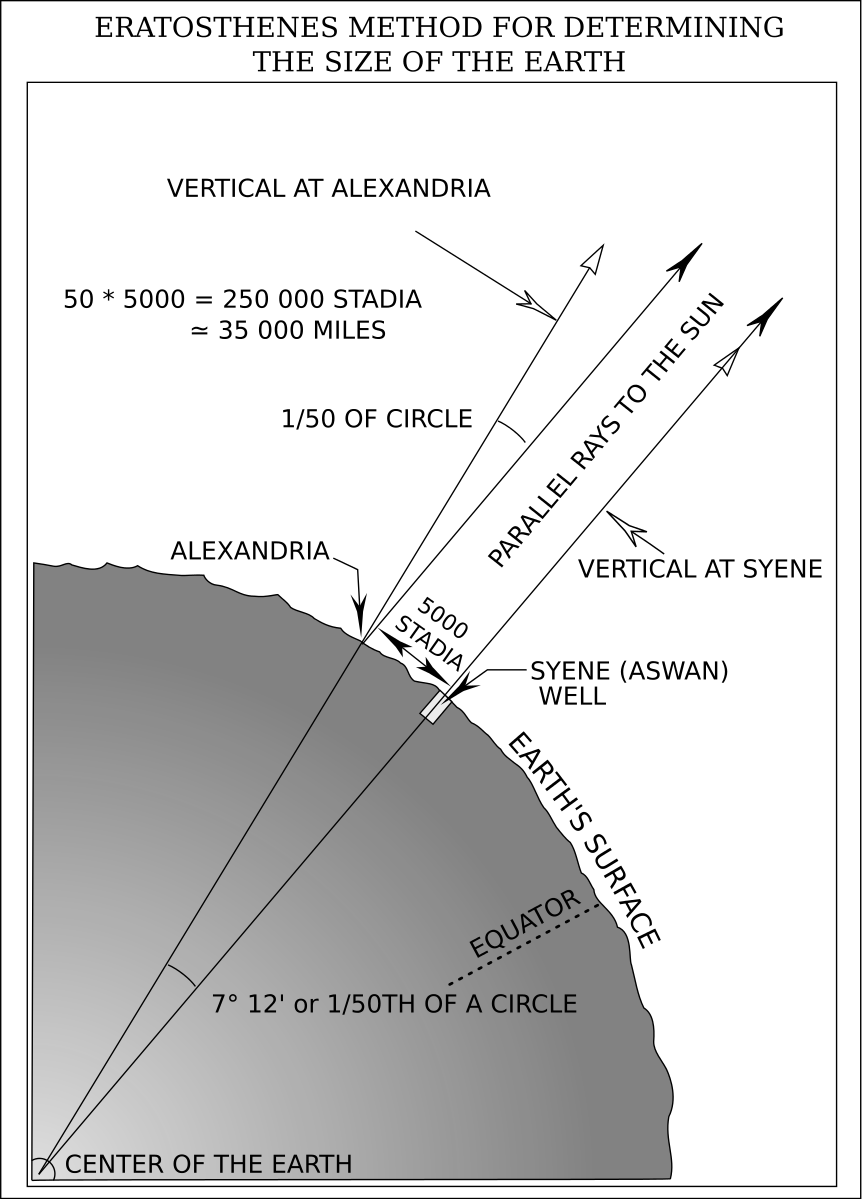
Eratosthenes (276-294 BC) measured the size of the Earth by noting that the angle between Syene and Alexandria is 1/50 of a circle, or 7.2 degrees. He also knew the distance between the cities, which enabled him to calculate the circumference of the Earth.
360 degrees
Earth circumference = Distance between Syene and Alexandria * ----------------- = 800 km * 50 = 40000 km
7.2 degrees
 |
 |
|---|---|
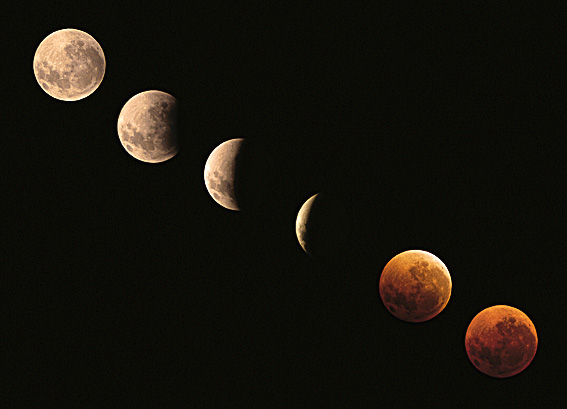
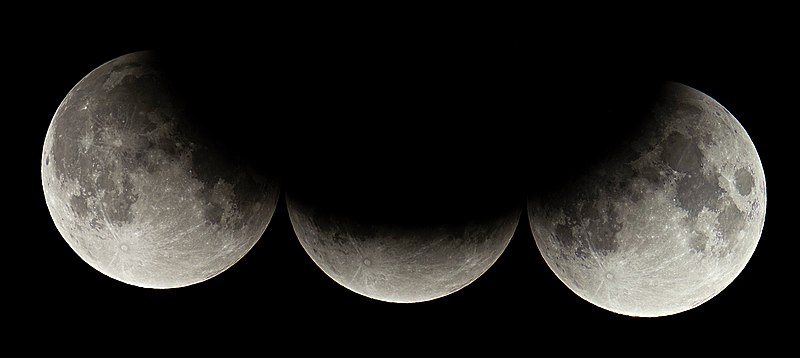
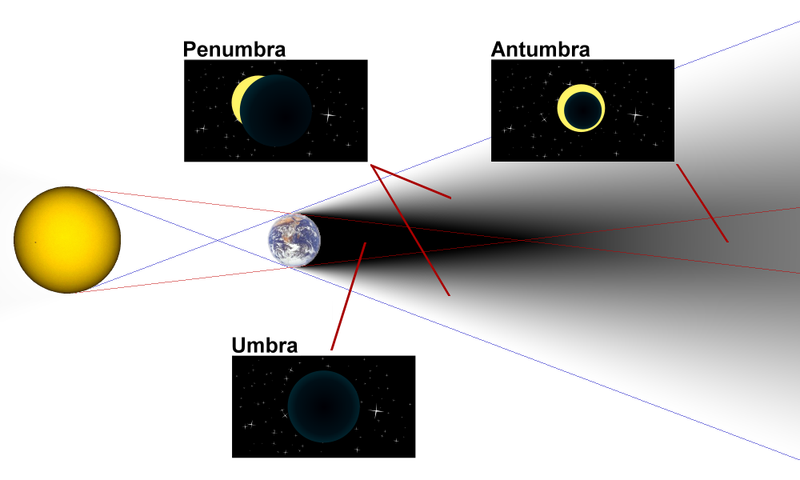
In the images, the moon passes through the Earth's shadow.
Aristarchus (310 BCE - 230 BCE) used a lunar eclipse to measure the size of the moon relative to the size of the Earth.
If the moon is larger than the Earth, then the Earth's shadow on the moon would be a spot smaller than the moon.
If the moon is smaller than the Earth, then the Earth's shadow on the moon will be a crescent. This is what turns out to be the case.
The moon's shadow on the Earth is small compared to the Earth.
 |
|---|
Aristarchus found that
Size of moon ~ 1/3 Size of Earth
The distance to the moon can be estimated by using Eratosthenes' measurement of the size of the Earth and the angular size of the moon.
Earth radius = 6371 km Moon radius = 1737 km = .273 Earth radii Moon distance = 384399 km = 60.3 Earth radii Moon angular size = .00905 rad = .519 degrees Moon angular size = 2 * Moon radius / Moon distance
 |
|---|
The shadow of the Earth on the moon is not sharp because of the penumbra.
 |
|---|
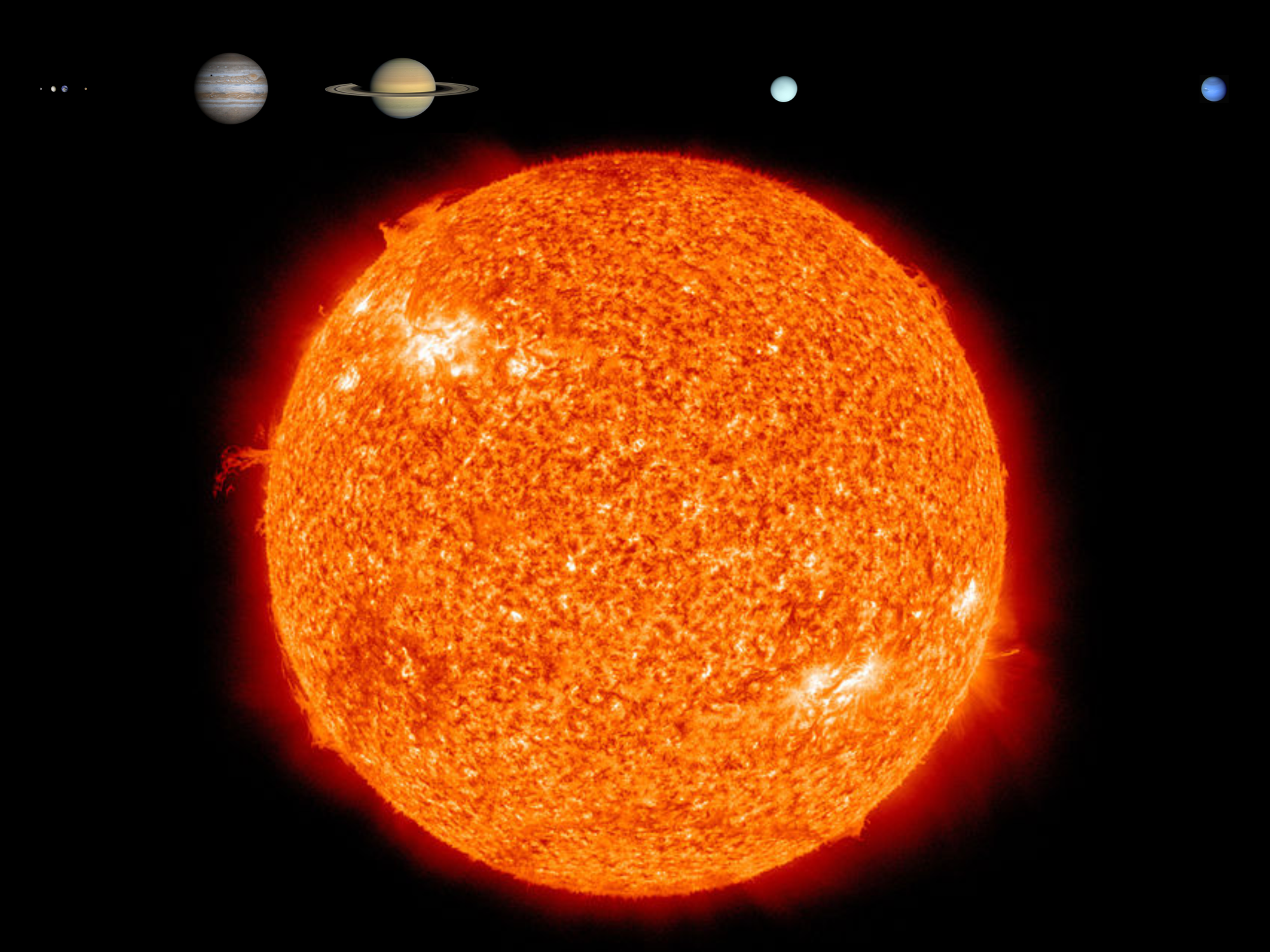
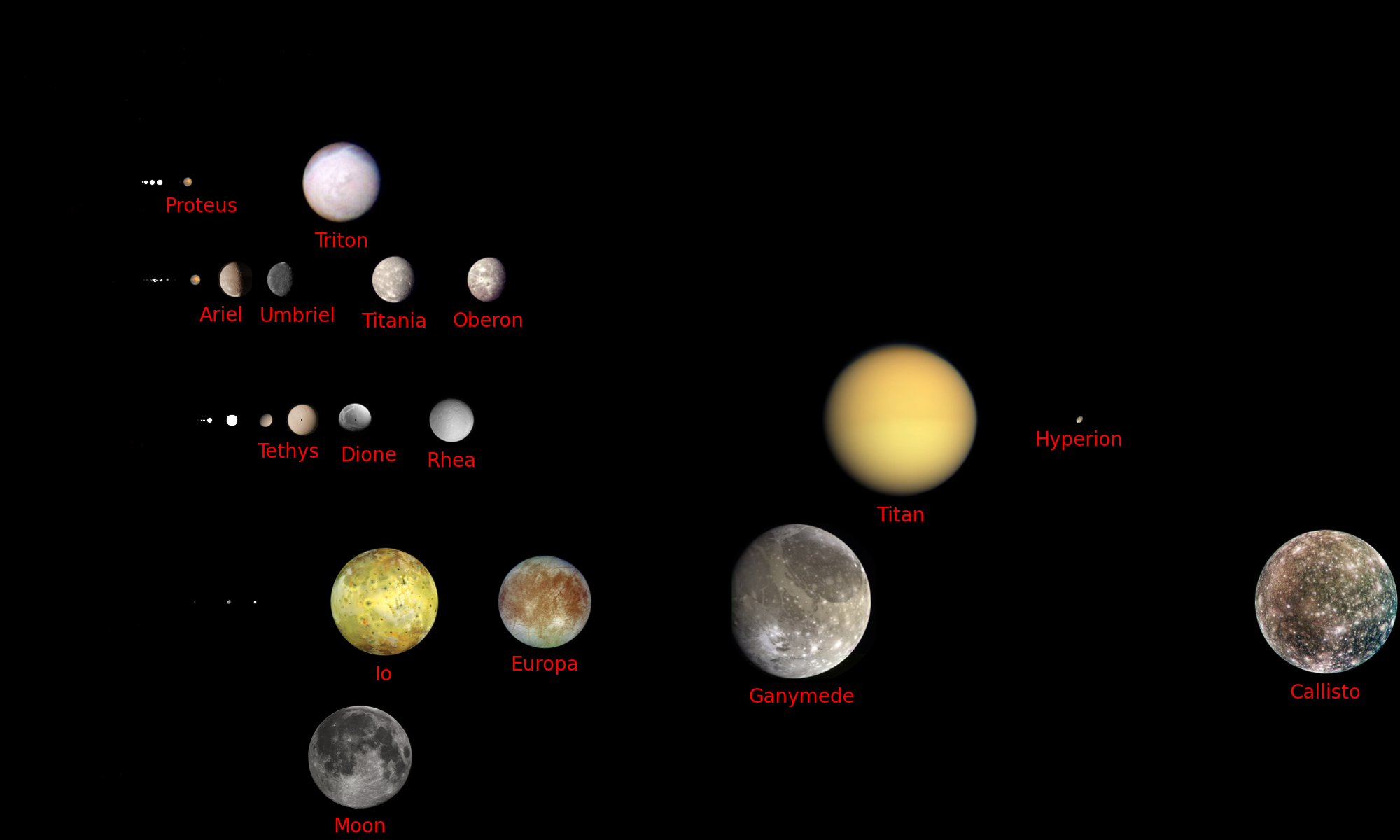
Sizes and distances to scale.
Sizes to scale. Also, the distances between planets are to scale.
 |
|---|
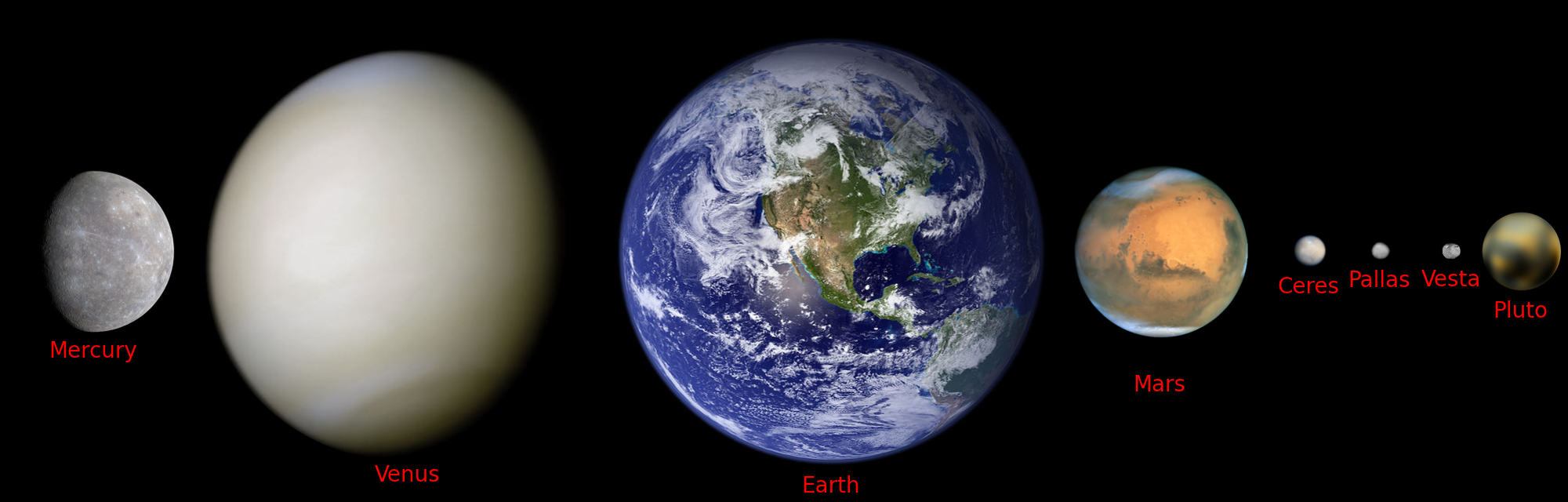
Sizes to scale.
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
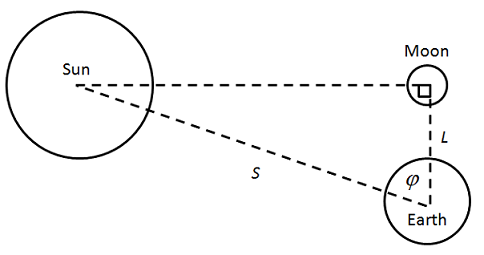
Aristarchus observed the moon when the Moon-Earth-Sun angle is a right angle.
If the sun is infinitely far away then the moon appears exactly half-lit. If the sun is at a finite distance then the moon appears more than half-lit.
In Aristarchus' time, telescopes didn't exist and only an approximate estimation was possible, but he was able to show that the sun is at least 20 times more distant than the moon.
 |
|---|
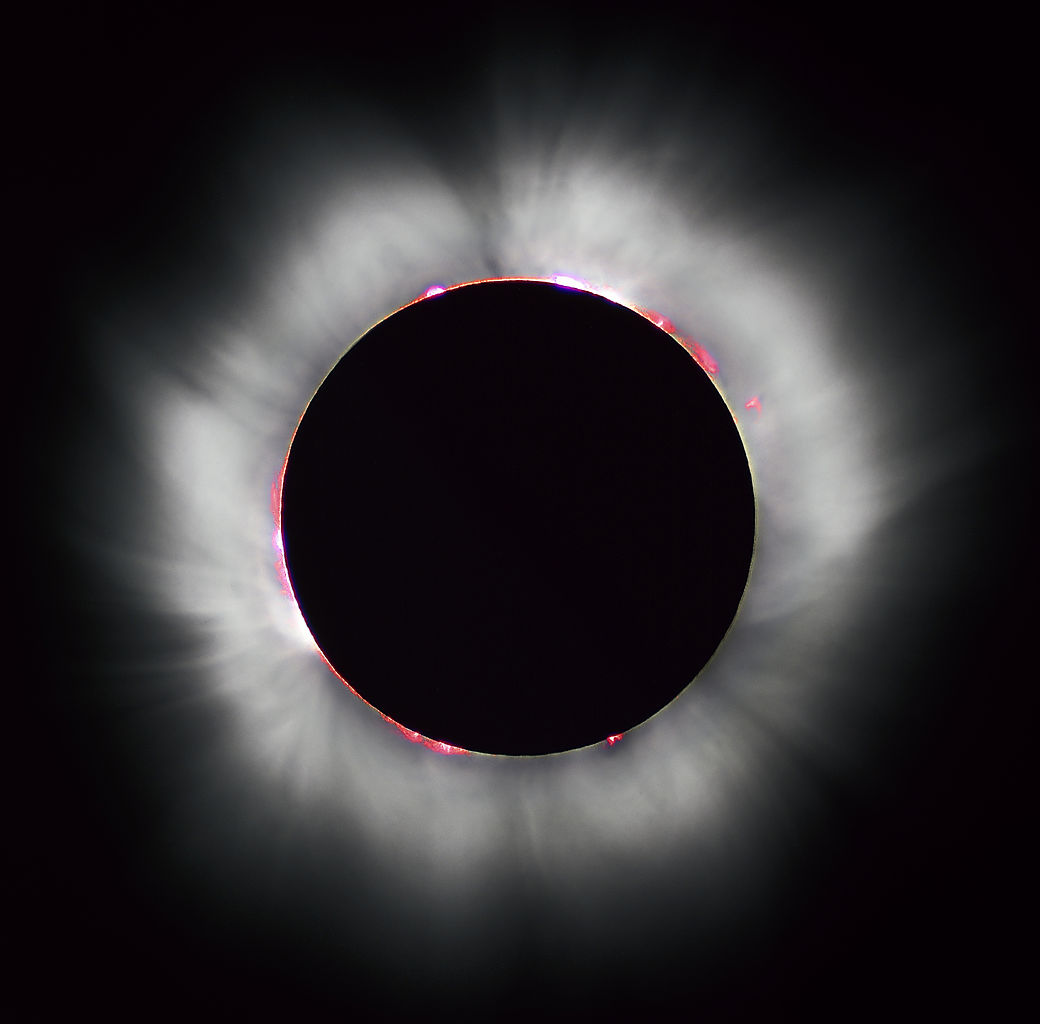
A solar eclipse tells us that the sun and moon have the same angular size.
Sun diameter = Moon diameter * Distance to sun / Distance to moonUsing this, Aristarchus estalished that the minimum size for the sun is
Sun diameter > 1/3 Earth diameters * 20
> 7 Earth diameters
This estalished that the sun is larger than the Earth and was the first solid
clue for heliocentrism.
The measurement of the distance to the sun was refined by Aryabhata (476 CE - 550 CE).
 |
 |
|---|---|
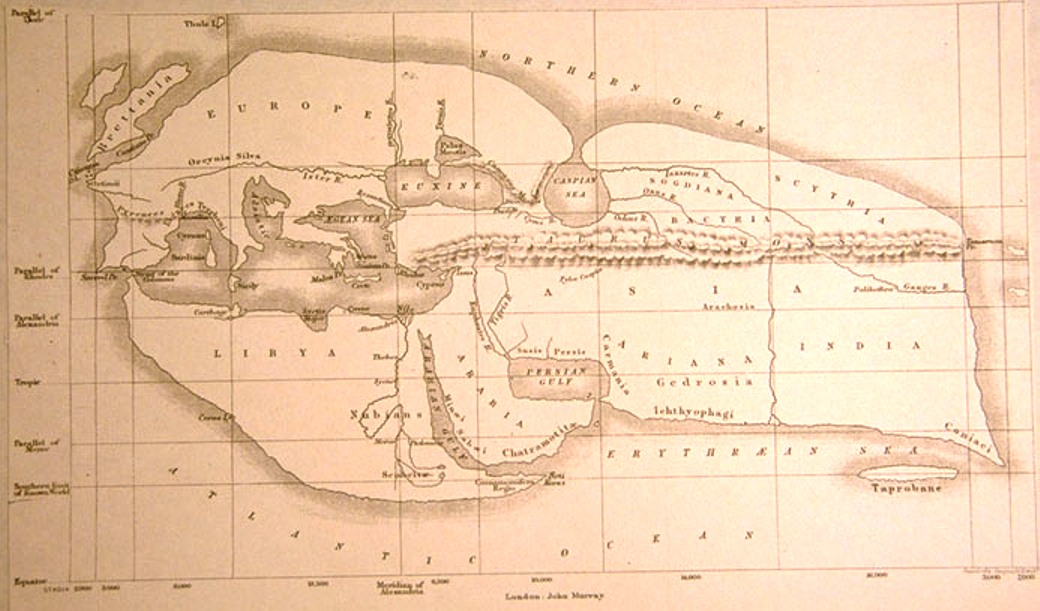
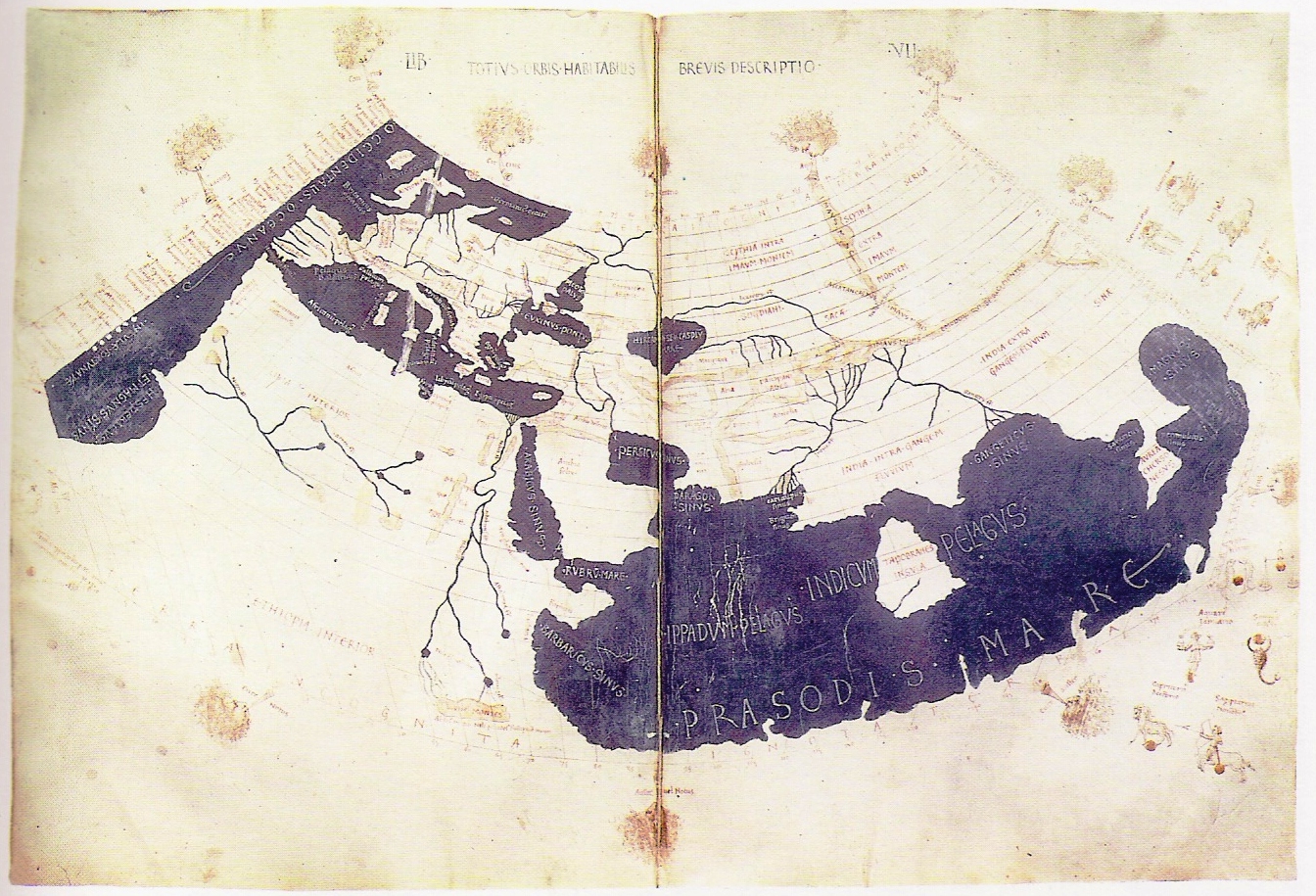
Ptolemy developed a system of latitude and longitude for mapping the world. His map covered 1/4 of the globe and was the standard until the Renaissance.
-310 -230 Aristarchus. Measures the distance to the sun.
-276 -195 Eratosthenes
-240 Eratosthenes measures the Earth's circumference to 20% error.
90 168 Ptolemy
476 550 Aryabhata. Refines the measurement of the distance to the sun.
1473 1543 Copernicus
1546 1601 Brahe
1600 Brahe measures accurate positions for the stars and planets over a period of 10 years.
1608 Lippershey invents the telescope
1609 Galileo builds a telescope
1609 Kepler uses Brahe's data to establish that planets orbit in ellipses.
1610 Galileo discovers the moons of Jupiter.
1639 Horrocks measures the transit of Venus, producing a value for the
distance to the sun that was low by a factor of 1/2.
1571 1630 Kepler
1564 1642 Galileo
1643 1727 Newton
1670 Picard measures the size of the Earth accurate to 1%.
1672 Richter and Cassini measure the parallax of Mars, which yielded a
value for the distance to the sun accurate to 10%.
1676 Romer uses the moons of Jupiter to measure the speed of light.
1729 Bradley measures the deflection of starlight due to the Earth's motion,
which gives a measurement for V/C, where V is the Earth's velocity.
1849 Fizeau makes the first measurement of the speed of light that doesn't
require astronomical data. 5% error.
1862 Focault measures the speed of light to .2% error.
1863 First measurements of stellar parallax and the distance to nearby stars.
2003 WMAP mission measures the Hubble constant to 5% precision.
Previous to this, the Hubble constant had an error of ~ 20%.
R = Earth-sun distance
V = Earth orbital velocity
T = Earth orbital time (1 year)
= 2 Pi R / V
t = Time for light to cross the Earth's orbit
= 2 R / C
C = Speed of light
Brahe's data consisted of measurements of angles between different objects.
This data could be used to establish the shape of orbits but not their size.
For example, if the size of the solar system were doubled along with the speeds of the
planets, the angles would stay the same and you wouldn't be able to tell the difference.
In 1639, Horrocks used a transit of Venus to measure the distance to the sun, but this method is incapable of giving an accurate value, and it can only be done once per century.
In 1672, Richter and Cassini measured the parallax of Mars which gives a result for the distance to the sun that is more accurate than the Venus method. The Mars method has an advantage over the Venus method in that it can be done once every 26 months, when Mars is at closest approach.
In 1676, Romer used the moons of Jupiter to measure the time it takes for light to cross the Earth's orbit. This gives a value for R/C.
In 1729, Bradley measured the deflection of starlight due to the Earth's motion, which gives a measurement of V/C, or equivalently, a measurement of R/C.
In 1849, Fizeau produced the first measurement for the speed of light that was independent of the Earth-sun distance R.
According to the Hubble law, distant galaxies recede from us with a speed of
Speed of galaxy = Hubble constant * DistanceSpeed is easy to measure (from the redshift) and distance is difficult to measure. Previous to 2003, the value of the Hubble constant was not well determined.
 |
|---|
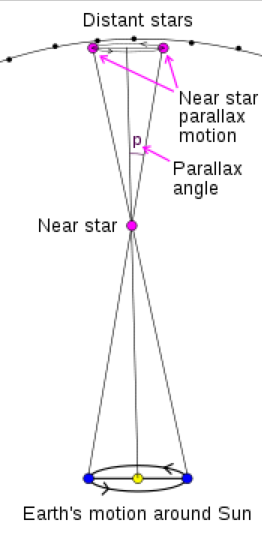
Resolution of human vision 60 arcseconds Resolution of a 10 cm telescope 1.0 arcseconds Parallax of Alpha Centauri 1.4 arcseconds Nearest star Parallax of 61 Cygni .31 arcsecondsSince the parallax of stars is undetectable to human vision, an astronomer in Ancient Greece could conclude that the stars are vastly more distant than the sun.
First parallax measurements were done in 1838, when Bessel measured the parallax of 61 Cygni, and Struve & Henderson measured the parallax of Alpha Centauri.
The limit of telescope resolution is 1 arcsecond due to air turbulence.
 |
|---|